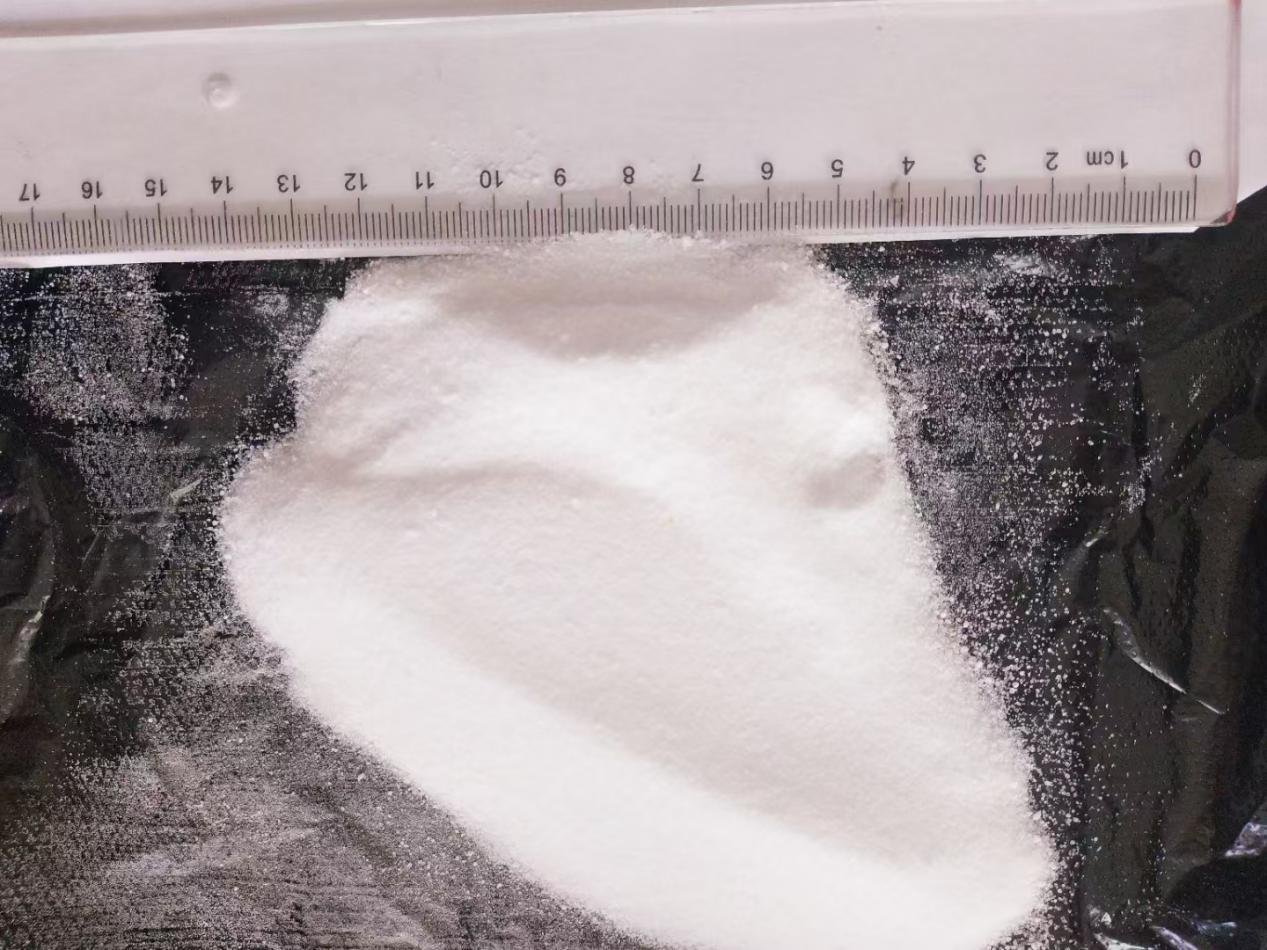
Potassium nitrate (KNO₃), a highly efficient, chloride-free compound fertilizer (13.5% nitrogen, 46% potassium), combines rapid nutrient delivery with environmental friendliness. Its unique nitrogen-potassium synergistic effect has made it a key choice for global agricultural production. Its core benefits include:

1. Promoting Crop Health
Providing nitrate nitrogen (NO₃⁻) and potassium (K⁺), rapidly enhances plant photosynthesis. Nitrate nitrogen can be directly absorbed by crops, preventing soil salt accumulation; potassium enhances stress tolerance (such as drought and lodging resistance) and significantly improves fruit sugar content and color.
2. Soil-Friendly
Potassium nitrate's chloride-free and low-sodium properties prevent soil salinization, making it particularly suitable for long-term continuous cropping. Studies have shown that continuous application of potassium nitrate can increase the soil aggregate structure improvement rate by 15%.
3. Precise Nutrition
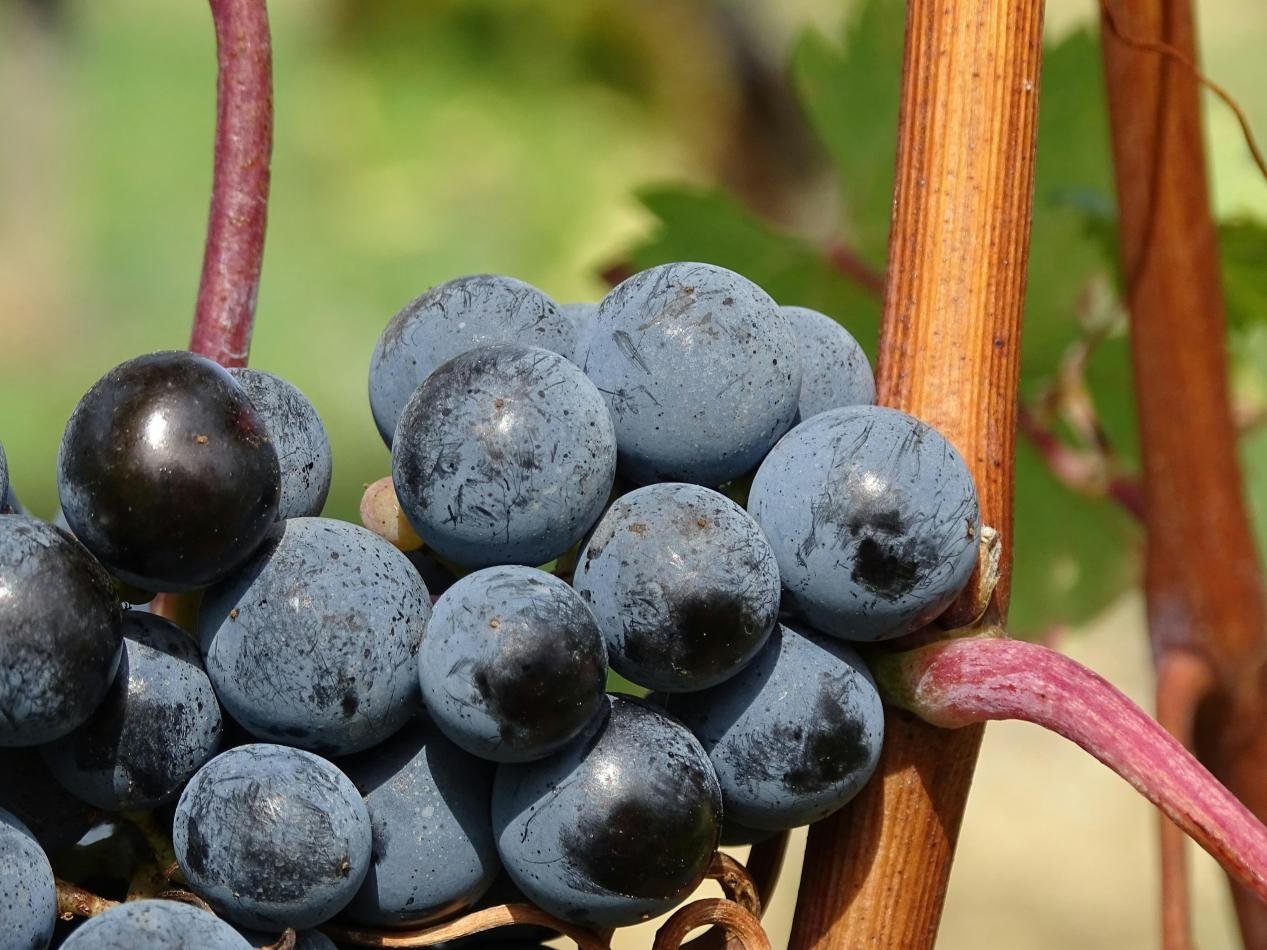
A nitrogen-potassium ratio of approximately 1:3 is ideal for meeting the needs of various crops at different growth stages. For example, it can increase grape fruit weight by 20% during the fruit-bearing stage.
Scientific Usage Instructions
Applicable Scenario: Topdressing is preferred for dry fields (avoid use in paddy fields). Applications can be made by flushing, drip irrigation (recommended concentration 0.3%-0.5%), or foliar spraying (recommended concentration 1%).
Critical Periods: Effective during the middle and late stages of crop growth, such as during fruit expansion (10-15 kg/mu for apples) and color change (5 kg/mu for grapes).
Note: Nitrogen dosage should be controlled during the late stages of fruit coloring to prevent excessive nitrogen from delaying ripening. In winter, it is recommended to combine with humic acid to mitigate the effects of heat absorption.
Applicable Crops and Benefits
Fruits: Grapes, strawberries, citrus, etc. It can increase sugar content by 2-3 percentage points, extending shelf life.
Cash Crops: Tobacco, tea, cotton, etc. It can enhance stress resistance and significantly improve quality. For example, the proportion of high-quality tobacco leaves in flue-cured tobacco can be increased by 12%.
Crops Resistant to Chlorine: Potatoes, onions, etc. It can prevent chloride ion toxicity and maintain yield and taste.