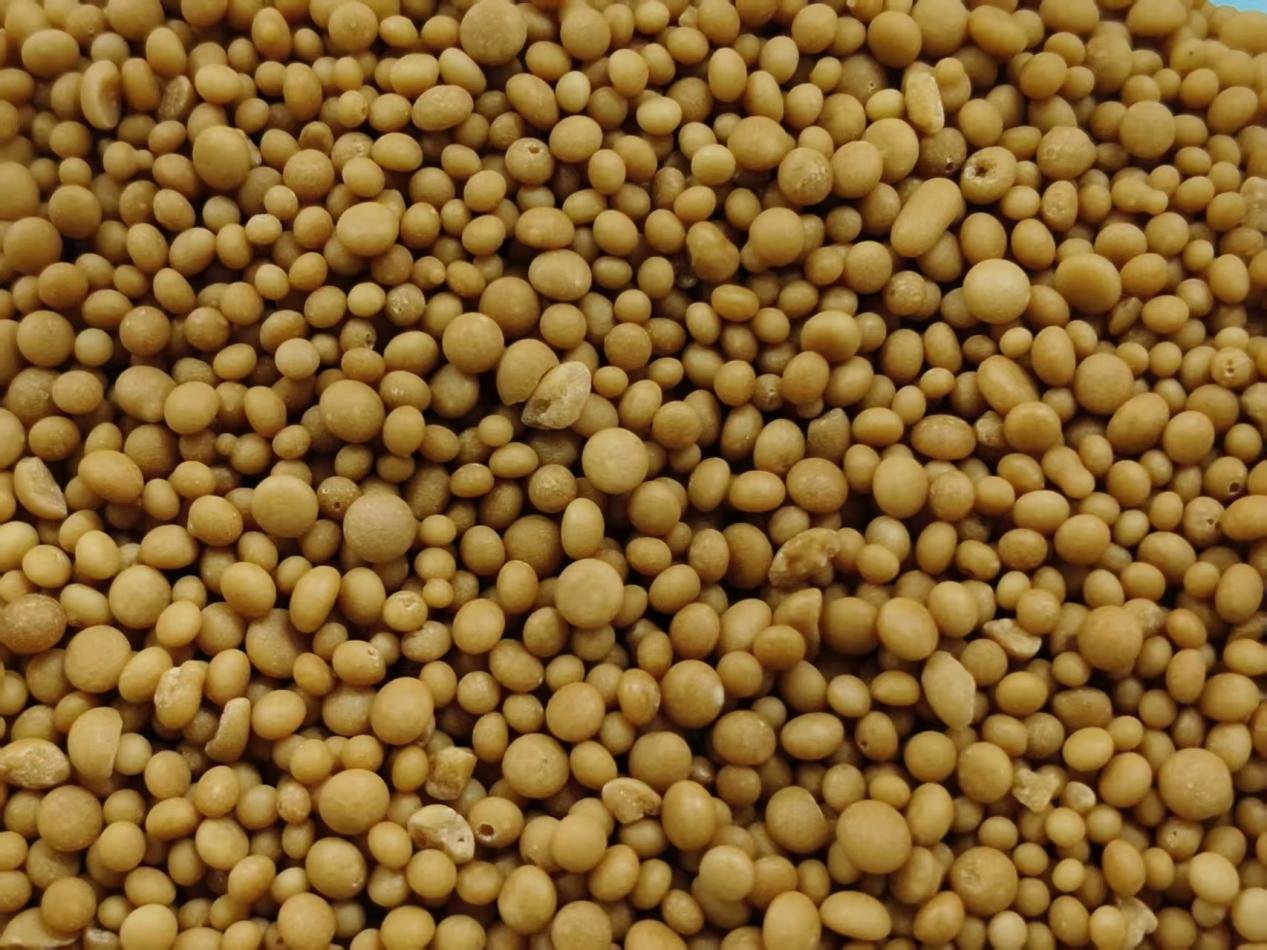
Tower granulation compound fertilizer is produced using the "melt tower granulation process." Its core process involves melting and mixing nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium at high temperatures, then cooling them through a tower spray process to form granules. This granulation technology is considered one of the most advanced in the global compound fertilizer industry.

Characteristics of High-Tower Granulated Compound Fertilizers
1. Uniform granules with a smooth, round appearance: Because the melt is naturally cooled and formed, the granules are uniform in size, round in shape, and bright in color.
2. Uniform nutrient content and high nutrient content: Thorough mixing in the melt ensures that each fertilizer granule has a nearly uniform nutrient content. High concentrations, such as over 45%, are typically achieved.
3. Contains trace elements and has good rapid release: The melt state facilitates the addition of trace elements (such as boron and zinc). Furthermore, the nitrogen in the fertilizer is primarily in the form of fast-acting ammonium and amide nitrogen. The fertilizer also contains a high content of water-soluble phosphorus, making it easily absorbed by crops and delivering rapid results.
4. Porous Granules for Fast Dissolution: During the cooling and solidification process, tiny pores naturally form within the granules ("pinholes" are one of their main appearance characteristics). This increases the contact area between the fertilizer and the soil solution, making it dissolve faster than ordinary compound fertilizers.
5. Moderate Strength, Non-Clumping: The granules possess a certain degree of compressive strength, making them easy to transport and store. The smooth surface and uniform particle size prevent clumping.

Precautions for Using High-Tower Compound Fertilizer
1. It is not suitable for use as a seed fertilizer. High-Tower Compound Fertilizer has a high nutrient concentration and dissolves quickly. Direct contact with seeds can easily cause seed and seedling burn.
2. Avoid surface application. Deep application and covering with soil is recommended to prevent nutrient volatilization.
3. Control the dosage and avoid overdosing. Due to its rapid effect and high concentration, applying too much at once can easily cause crops to grow too tall or fall over.
4. Water promptly, but avoid heavy flooding. After application to the soil, an appropriate amount of water is needed to dissolve and migrate the fertilizer so that it can be absorbed by the roots. However, excessive flooding can cause nutrients to leach into the deeper soil layers, resulting in waste and environmental pollution.
Summary: High-tower granulated compound fertilizers are characterized by high nutrient content, excellent physical properties, balanced nutrient release, ease of application, and suitability for mechanized applications. When using, care should be taken to avoid direct contact with crop roots, separate the fertilizer from the seed, and water the crops promptly.